This article describes how you can use Arcus' message handler concept with Azure Functions; allowing you to more easily port your business logic from/to Azure Functions.
Azure EventHubs message handling for Azure Functions
Our EventHubs message pump system provides a way to receive incoming events, but this is not needed in an Azure Functions environment. Today, Azure Functions acts as a message receiver meaning that the function is triggered when an event is available. Azure Functions has no out-of-the-box way to provide a clean implementation for handling different types of messages that are received. If you want to do that, you'll need to write all plumbing code yourself. With Arcus.Messaging, we provide this for you so that you can focus on writing the actual business logic.
Following terms are used:
- Message handler: implementation that processes the received event from an Azure EventHubs subscription. Message handlers are created by implementing the
IAzureEventHubsMessageHandler<TMessage>. This message handler will be called upon when an event is available on the Azure EventHubs subscription. - Message router: implementation that delegates the received Azure EventHubs event to the correct message handler.
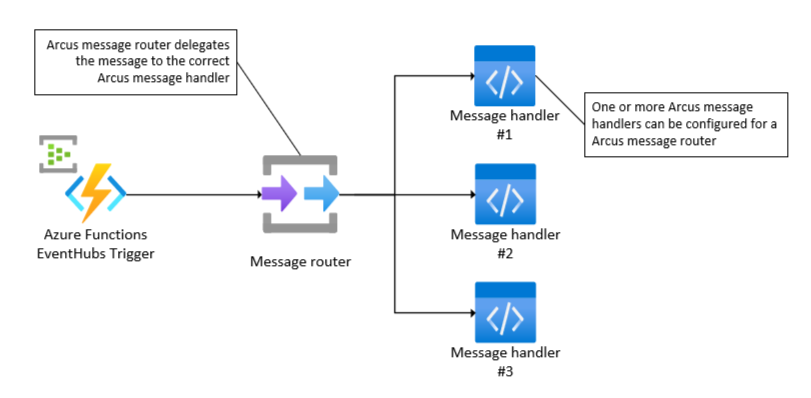
We will walk you through the process of using message handlers with Azure Functions:
Installation
To use the following described features, install the following package:
PM > Install-Package -Name Arcus.Messaging.AzureFunctions.EventHubs
Receive Azure EventHubs message in an Azure Function
Here's an example of how an Azure Function receives an Azure EventHubs message from a topic:
public class SensorReadingFunction
{
[Function("sensor-reading")]
public async Task Run(
[EventHubTrigger("sensors", Connection = "EventHubsConnectionString")] string[] messages,
Dictionary<string, JsonElement>[] propertiesArray,
FunctionContext context)
{
// Processing events...
}
}
Declaring our Azure EventHubs message handlers
Registering message handlers to process the EventHubs events is fairly easy to do.
⚡ You can use the same message handlers in an Azure Functions an a .NET Worker message pump scenario.
Processing sensor reading updates:
public class SensorReadingUpdateEventHubsMessageHandler : IAzureEventHubsMessageHandler<SensorReadingUpdate>
{
private readonly ILogger _logger;
public SensorReadingUpdateEventHubsMessageHandler(ILogger<SensorReadingUpdateEventHubsMessageHandler> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task ProcessMessageAsync(
SensorReadingUpdate readingUpdate,
AzureEventHubsMessageContext messageContext,
MessageCorrelationInfo correlationInfo,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Processing sensor reading {SensorId} in room {Room}", readingUpdate.SensorId, readingUpdate.RoomName);
}
}
Processing sensor config updates:
public class SensorConfigUpdateMessageHandler : IAzureEventHubsMessageHandler<SensorConfigUpdate>
{
private readonly ILogger _logger;
public SensorConfigUpdateMessageHandler(ILogger<SensorConfigUpdateMessageHandler> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task ProcessMessageAsync(
SensorConfigUpdate configUpdate,
AzureEventHubsMessageContext messageContext,
MessageCorrelationInfo correlationInfo,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
log.LogInformation("Processing sensor config {SensorId} in room {Room}", configUpdate.SensorId, configUpdate.Room);
}
}
Now that we have created our message handlers, we can declare when we should use them by registering them with our router.
Processing received messages through the message router
Now that everything is setup, we need to actually use the declared message handlers by routing the events from the Azure Function into the correct message handler.
To achieve that, we need to add message routing with the .AddEventHubsMessageRouting extension:
Isolated Azure Functions
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
var host = new HostBuilder()
.ConfigureFunctionsWorkerDefaults(builder =>
{
builder.Services.AddEventHubsMessageRouting()
.WithEventHubsMessageHandler<SensorReadingUpdateMessageHandler, SensorReadingUpdate>()
.WithEventHubsMessageHandler<SensorConfigUpdateMessageHandler, SensorConfigUpdate>();
})
.Build();
host.Run();
In-Process Azure Functions
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
[assembly: FunctionsStartup(typeof(Startup))]
namespace SensorReading
{
public class Startup : FunctionsStartup
{
public override void Configure(IFunctionsHostBuilder builder)
{
builder.AddEventHubsMessageRouting()
.WithEventHubsMessageHandler<SensorReadingUpdateMessageHandler, SensorReadingUpdate>()
.WithEventHubsMessageHandler<SensorConfigUpdateMessageHandler, SensorConfigUpdate>();
}
}
}
This extension will register an IAzureEventHubsMessageRouter interface that allows you to interact with the registered message handlers in a easy manner.
⚡ It also registers an more general
IMessageRouteryou can use if the general message routing (with the event' raw body asstringas input) will suffice.
We can now inject the message router in our Azure Function and process all events with it. This will determine what the matching message handler is and process it accordingly:
Isolated
using Arcus.Messaging.Abstractions.EventHubs;
using Azure.Messaging.EventHubs;
public class SensorReadingFunction
{
private readonly IAzureEventHubsMessageRouter _messageRouter;
public SensorReadingFunction(IAzureEventHubsMessageRouter messageRouter)
{
_messageRouter = messageRouter;
}
[Function("sensor-reading")]
public async Task Run(
[EventHubTrigger("sensor-reading", Connection = "EventHubsConnectionString")] string[] messages,
Dictionary<string, JsonElement>[] propertiesArray,
FunctionContext executionContext)
{
_logger.LogInformation("First EventHubs triggered message: {Message}", messages[0]);
for (var i = 0; i < messages.Length; i++)
{
string eventBody = messages[i];
Dictionary<string, JsonElement> eventProperties = propertiesArray[i];
EventData eventData = CreateEventData(message, eventProperties);
AzureEventHubsMessageContext messageContext = eventData.GetMessageContext("<namespace>", "$Default", "<eventhubs-name>");
using (MessageCorrelationResult result = executionContext.GetCorrelationInfo(eventProperties))
{
await _messageRouter.RouteMessageAsync(eventData, messageContext, result.CorrelationInfo, CancellationToken.None);
}
}
}
private static EventData CreateEventData(string eventBody, IDictionary<string, JsonElement> properties)
{
var data = new EventData(eventBody);
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, JsonElement> property in properties)
{
data.Properties.Add(property.Key, property.Value.ToString());
}
return data;
}
}
In-Process
using Arcus.Messaging.Abstractions;
using Arcus.Messaging.Abstractions.EventHubs;
using Arcus.Messaging.Abstractions.EventHubs.MessageHandling;
using Arcus.Messaging.AzureFunctions.EventHubs;
public class SensorReadingFunction
{
private readonly IAzureEventHubsMessageRouter _messageRouter;
private readonly AzureFunctionsInProcessMessageCorrelation _messageCorrelation;
public SensorReadingFunction(
IAzureEventHubsMessageRouter messageRouter,
AzureFunctionsInProcessMessageCorrelation messageCorrelation)
{
_messageRouter = messageRouter;
_messageCorrelation = messageCorrelation;
}
[FunctionName("sensor-reading")]
public async Task Run(
[EventHubTrigger("sensors", Connection = "EventHubsConnectionString")] EventData[] events,
ILogger log,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
foreach (EventData message in events)
{
log.LogInformation($"First Event Hubs triggered message: {message.MessageId}");
var messageContext = message.GetMessageContext("sensor-reading.servicebus.windows.net", "$Default", "sensors");
// W3C message correlation (with built-in Microsoft dependency tracking, recommended).
using (MessageCorrelationResult result = _messageCorrelation.CorrelateMessage(message))
{
await _messageRouter.RouteMessageAsync(message, messageContext, result.CorrelationInfo, cancellationToken);
}
// Hierarchical message correlation (without built-in Microsoft dependency tracking).
MessageCorrelationInfo correlationInfo = message.GetCorrelationInfo();
await _messageRouter.RouteMessageAsync(message, messageContext, correlationInfo, cancellationToken);
}
}
}
Upon receival of an Azure EventHubs event, the event will be either routed to one of the two previously registered message handlers.